In a Hyper-V host, the MAC addresses received by the VM’s network adapters are dynamic and are defined by the range of the host. I don’t want to repeat myself, I have written an article on this subject.
Using Windows 10: Connect to a network. This method is only applicable if you are currently. This can be used to get mac address for remote computers also. Below are few examples on how to use this command. It works on XP, Vista, Windows 7, Server 2003 and Server 2008 operating systems. Get mac addresses from CMD. Just run the command getmac to get the mac addresses. Find an example below.

However, there are several cases that we need to have a static MAC address on a VM. For example, when we want to do DHCP Filtering or DHCP Reservations, or if an inventory service or even some application’s license is linked to a MAC address. In such a case, when we move the VM to another Hyper-V host, it must keep the same MAC address. Otherwise, if it had a dynamic address then it would get a new one.
Let’s see how we set a static MAC address to a VM in Hyper-V. As always, this can be done either through Hyper-V Manager or PowerShell.
Set static MAC address using Hyper-V Manager
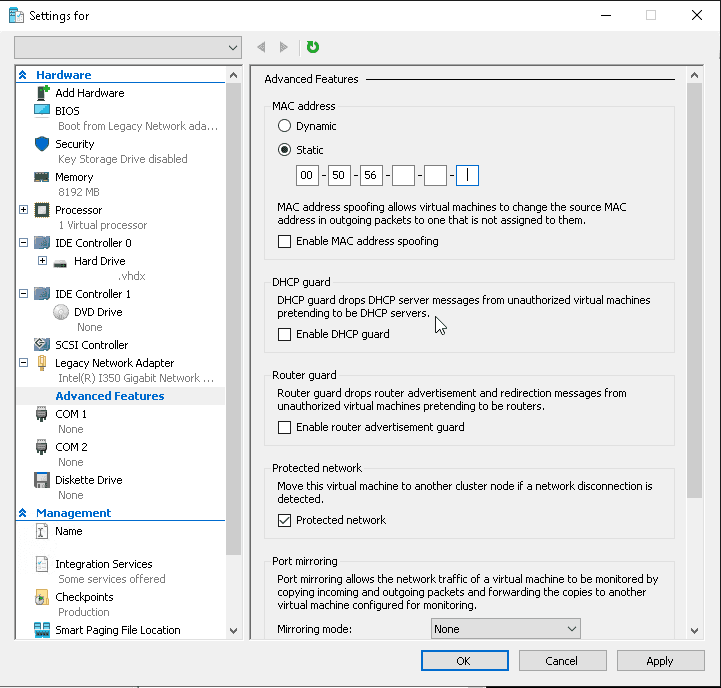
First, make sure the VM is not running.
Open Hyper-V Manager and then VM settings. Here, expand the Network Adapter and go to Advanced Features.
To set the VM with a static MAC address, enable the Static option and enter the address you want.
Set static MAC address using PowerShell
This is done using the Set-VMNetworkAdapter cmdlet as you can view below.
Set-VMNetworkAdapter -VMName SRV01 -StaticMacAddress “00112233445566”
Finally, note that when you set up a static MAC address for a VM, be sure it is not within the dynamic address range generated by the Hyper-V host. If it is within the range, then it is possible to give the same address to another VM as the host does not control the management between static and dynamic addresses.
Related posts:
 -->
-->Mac Address Explained
This article provides a solution to an issue where users in a different subnet are unable to connect to the virtual server after a failover from one cluster node to another.

Original product version: Windows Server 2012 R2
Original KB number: 244331
Symptoms
After a failover from one cluster node to another, users in a different subnet may be unable to connect to the virtual server.
Cause
Server Clusters in Windows 2003 Enterprise Server or Datacenter Server, Failover Clustering in Windows Server 2008 Enterprise or Datacenter and Failover Clustering in Windows Server 2008 R2 Enterprise or Datacenter performs a gratuitous Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) request when a failover occurs. However, some devices (such as switches) may not forward the gratuitous ARP request to other devices. This causes devices on the other side of the switch or router to have the incorrect MAC address for the virtual server that has failed over. Often, this situation corrects itself after a router or switch sees the failure and updates its ARP cache by performing a broadcast. Most routers and switches are configured not to forward ARP traffic between subnets to prevent ARP storms from occurring.
Resolution
Gratuitous ARP requests must be forwarded across networks so that all devices receive the updated MAC-to-IP address mappings. Contact your hardware manufacturer for information about how to change your switch or router's configuration so that gratuitous ARP requests are passed to all networks.
Mac Address For Printer Server
More information
In a cluster, each computer (or cluster node) has a network adapter attached to the corporate network, and each cluster node has its own IP address, network name (NetBIOS name), and MAC address. The virtual server has an IP address and network name, but uses the MAC address of the cluster node that is the current owner of the virtual server resources.
169017 Information on Groups and Resources Using Microsoft Cluster Server
When a failover occurs, the cluster server of the node that is receiving IP resources sends a gratuitous ARP request so that all devices (computers, routers, and switches) are updated, and a new MAC address is assigned to an existing IP address. If a switch or router does not pass the updated MAC-to-IP address mappings, other network devices contain the old MAC address for the cluster node that is down.
For additional information, click the article numbers below to view the articles in the Microsoft Knowledge Base:
199773 Behavior of Gratuitous ARP in Windows NT 4.0
168567 Clustering Information on IP Address Failover
